A weighty hardware organization started mining a bizarre shaded stone at Thousand years Mine in northern Alberta in 2011.
His manager immediately understood that they had something uniquely great, Michael Greshko reports for Public Geographic. He quit looking all the more carefully and astounded the material, which had peculiar examples.

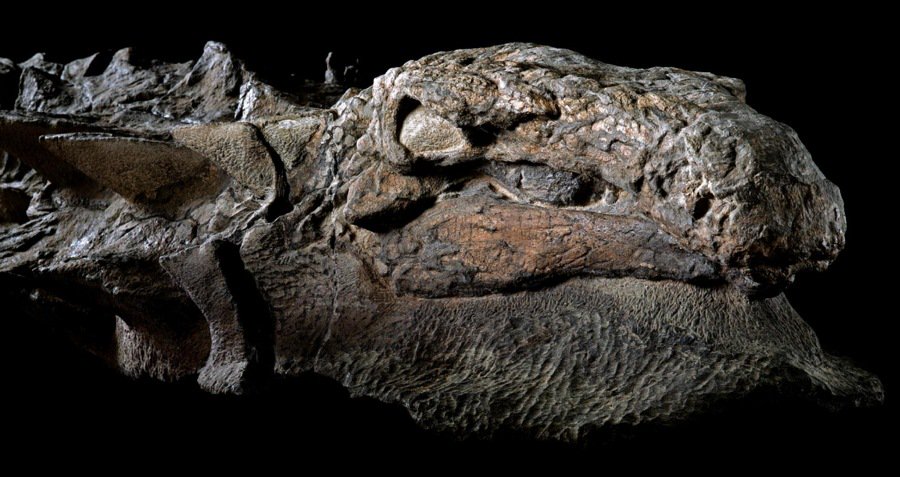
A little fossilized skin had as of late been separated from a shielded nodosaur, a sort of ankylosaur. By and by, this was not only a fossil; it was one of the most outstanding safeguarded examples of nodasaurus at any point found.
The fossil remaining parts are staggeringly exact, looking like a dozing mythical serpent.
As per Public Geographic, which supported the five-year, 7,000-hour readiness of the fossil, almost certainly, the 3,000-pound,18-foot-long animal kicked the bucket in or close to a stream. Then, at that point, its swollen body drifted out to the ocean prior to sinking back-first into the grime where fossilization started.
“It’s fundamentally a dinosaur mummy — it truly is extraordinary,” Wear Brinkman, overseer of conservation and exploration at the Regal Tyrrell Historical center where the fossil is housed tells Craig S. Smith at The New York Times.
The striking conservation of its shielded plates, as well as a few safeguarded scales, are assisting paleontologists with at long last figuring out the size and state of the animal’s keratin guards.
“I’ve been calling this one the Rosetta stone for defensive layer,” Donald Henderson, custodian of dinosaurs at the Tyrrell Exhibition hall tells Greshko.

As Matt Rehbein at CNN reports, the dino is 110 million years of age, making it the most seasoned at any point tracked down in Alberta. It likewise addresses another sort and types of nodosaur. In any case, the most thrilling viewpoint might be at the minute level, Greshko reports.
The specialists have identified miniscule pieces of red shade, which could assist them with reproducing the dinosaur’s hue — a component that might have assisted it with drawing in mates.
“This reinforcement was obviously giving insurance, yet those explained horns on the facade of its body would have been practically similar to a bulletin,” Jakob Vinther, a creature tinge master from the College of Bristol who has concentrated on the fossil, tells Greshko.
The new example isn’t the main extraordinary ankylosaur example as of late disclosed. Simply last week Brian Switek at Smithsonian.com detailed that the Illustrious Ontario Gallery found another species in Montana, which they nicknamed Zuul. That example likewise has some flawless protection plates and skin as well as a tail club.
Switek makes sense of that during decay the protection plates of ankylosaurs normally tumble off and are many times washed away or not found.
In any case, the disclosure of these two unprecedented examples will go far towards assisting analysts with figuring exactly what these creatures resembled and how they utilized their considerable horns and covering.

The nodosaurus is presently in plain view at the Regal Tyrrell Gallery in Drumheller, Alberta, as a feature of a display featuring the significance of collaboration between extraction enterprises and scientistss in revealing fossils.





